Scaling UMA
This section explains how UMA is scaling to other EVM networks. The full list of supported networks can be found here.
How scaling UMA works on Polygon#
The UMA ecosystem comprises a dispute resolution layer — the Data Verification Mechanism (DVM), and the financial contracts it secures. UMA’s architecture has from conception been decoupled, meaning the dispute layer and the contract layer do not need to live on the same chain.
Having a decoupled architecture gives the advantage of being able to deploy to any EVM chain efficiently. Our scaling strategy allows the contract layer on any EVM chain to access the same DVM any contract native to Ethereum has access to.
UMA makes use of an arbitrary message bridge that allows for two-way messages to pass between the secondary EVM network and Ethereum mainnet. The message bridge typically uses the secondary network's Arbitrary Message system, meaning it can be as trusted as the EVM network itself.
The section below walks through how UMA's Optimistic Oracle is used as the arbiter of price requests natively on the Polygon network. If a request is made to the Polygon Optimistic Oracle and the proposal goes undisputed, the result is deemed the accepted outcome.
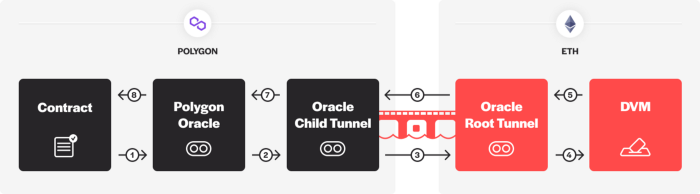
If the event is disputed, then the following steps will be taken to bridge the disputed result back to the final arbitrator, the DVM:
- A Polygon contract, such as a prediction market, needs a price to settle a payout. The contract expects to get this price from an optimistic oracle
Polygon Oracle. - For some reason, a user disagrees with the price returned by the
Polygon Oracleand disputes the price. - The disputed price request is passed from the Polygon Oracle to a contract called the
Oracle Child Tunnel, whose sole responsibility is to communicate with anOracle Root Tunnelon the Ethereum network. - The
Oracle Child Tunnelrelays the dispute to Ethereum mainnet to theOracle Root Tunnel. - The
Oracle Root Tunnelhas special permission to request a price from the DVM, where the familiar voting and resolution process is performed by UMA voting token holders. Once the DVM has resolved a price request, the outcome of the vote is pushed toOracle Root Tunnel. It is important to note that the DVM is not aware of which chain the request came from, nor does it need to. - Like before, the
Oracle Root Tunnelrelays the result from the DVM to theChild Tunnelon Polygon. - Finally, the
Oracle Child Tunnelthen sends a message back to thePolygon Oracle. - The outcome of the dispute is resolved and Polygon based contracts can now use the resolved price.
Resources#
For more information on how to launch a contract to Polygon, you can follow the tutorial.
If you want to know more about how UMA plans to scale to more scaling solutions you can read out article.